DESCRIPTION : Carpenter ants ( English : Carpenter ants ( black ants , big black ants ) are part of the family Formicidae , black and measuring between 6-13 mm.
Carpenter ants or spoils woods like moist places and usually attack parts support , columns verandas , thresholds , joists , the beams and window frames .

carpenter Ants Camponotus spp.
- Carpenter ants , like other ants belong to the same order as bees, wasps and bumblebees. There are morphological differences between species and adults of the same species ( Workers , queens, males) .
- In general , carpenter ants are black with a single stalk ( bump) at the center of its size.
- Males and females are very different. Males are from September to October mm long . Their small rounded head has beady eyes compounds and small mandibles. Their legs are weak. All males have two pairs of wings whose function is to transmit the seed.
- The queen is the most imposing of the ant colony. It is usually several times larger than the workers . They reach 18 mm in length.
- The workers are wingless females . They are between 6 and 13 mm long .
- The coupling of carpenter ants is in flight during the spring with a single male . The abdomen contains a queen spermatheca which receives the male sperm during mating and guards alive for several years.
- After dropping its wings, fertile queen looking for a suitable location for his colony. For example , a tree trunk or a piece of wood in a window or in the basement.
- The queen starts to lay the first workers . The duration of the design, from egg to adult ant varies from 48 to 74 days
- Ants are insects with complete metamorphosis with four larval stages.
- The larvae resemble small grubs and soft. They become prepupa , a white middle cylindrical shape and motionless body.
- A few days later they are transformed into white pupae and adults thereafter.
- Workers can live about seven years and the queen up to 17 years. And after 3-6 years , a colony can have up to 2000 workers or more.
- When the queen dies, the production of female stops and the colony disappears after 1 to 2 years.
- In the wood and foam insulation in the attic of the house , close to water sources.
- They make their nests in dead or hollow trees in moist or rotting wood .
- Nearly homes, they can live in telephone poles , picket fences , piles of wood debris or piles of firewood.
- infestations homes as cottages, are more common in forested areas .
- A mature colony has a main and satellite nests nest ( up to ten ) .
- The main nest, which houses the queen , eggs and larvae of the first stage is always located near a source of moisture.
- The satellite nests may contain mature larvae and pupae , and winged adults . Satellite nests are connected to the main nest in tunnels dug in the ground by the workers.
- Ants are omnivorous insects. They feed on the honeydew produced by aphids and other Homoptera , insects and small invertebrates living or dead , and juices of plants and various fruits.
- Food is often consumed locally by ants in charge of supplies, then regurgitated to the queen, larvae and other workers when they return to the nest.
- The workers move up to a hundred meters from their nest in search of food.
- In their natural habitat , carpenter ants are a food source for woodpeckers and other insectivorous birds . Bears attack trees harboring nests to eat the larvae and pupae .
- These insects are important decomposers of trees . When the colony disappears , fungi and bacteria then settled around these open spaces and degrade lignin and cellulose on large surfaces.
- Like many other species of ants, camponotes also dig the earth. They carry particles and small stones on the surface, thus providing a patch of soil .
Carpenter ants are not aggressive , but they can bite when handled .
The workers are more active at night and during the summer when it is hot. They often leave the colony in the late afternoon and buy their food at night , returning to the nest at dawn .
Carpenter ants find their way from the nest by the sight and smell. The camponotes seem to have a view more developed than other types of ants and they use visual cues to orient themselves. They also create chemical trails marking their path with fragrant substances called pheromones. That is why you see most of the time return to the same place.
Infestations in our homes by ants can occur in four ways:
- The arrival in the home of a queen who founded a new colony.
- The migration of a colony or part of the colony (satellite nest) after a major stress ( such as felling a tree, window replacement or disappearance of a fence wood where was the nest) .
- The introduction of material containing ants in the house , such as firewood.
- The formation of a satellite nest , without a queen ( the most common cause of infection in Quebec ) . Several cases of satellite nests were found in the window frames of basement and ground floor, in the attic, and in the foam insulation of exterior walls.
- Observation of ants active during the cold season . The insects are then looking for food and water.
- Observation winged adults emerged from the nest during the spring .
- To hear a slight rattle or swish created by the movement of countless insect legs in a structure.
- The presence of small clusters of sawdust tendencies to reappear in the same location as the input of the nest.
Here are ways to prevent the installation of a colony of carpenter ants in your home.
- Eliminate sources of moisture that can affect wood parts , repair pipes and leaky roofs , adequately ventilate the wet parts of the house.
- Eliminate the rotten wood around the house .
- Do not accumulate large pieces of wood near the foundation .
- Store firewood properly , by raising stacks logs from the ground .
- Place them far enough from buildings. Hit the wood for insects before falling into the house . Once entered the wood , inspect the heated logs and eliminate ants are active .
- Trim tree branches and shrubs so they do not touch or do not dominate the structure of the house ( ants can drop a branch to explore new territories ) . Repair and prune damaged trees , remove stumps.
- Inspect , clean and repair the gutters before the rains .
- Seal cracks in the siding of the house , check the foundations and caulk around doors and windows. Install screens on different openings , including vents.
- Do not leave any food attractive to ants
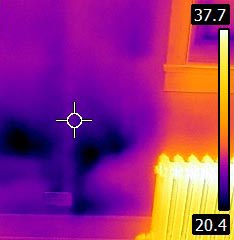
Thermography to detect water leaks
Imaging infrared thermography is a visualization tool surface temperature. Image interpretation can detect insulation problems or water infiltration and sometimes the presence of insect and rodent behind the walls (carpenter ants, wasps nest, rat, mouse ... tec.)
Water infiltration is largely responsible for infestations of carpenter ants, carpenter ants indeed need moist places to survive and to be able to dig their galleries in the wood.
 |
 |
The dark area represents the coldest places because of water infiltration in the window. Carpenter ants take the opportunity to expand their nest. |
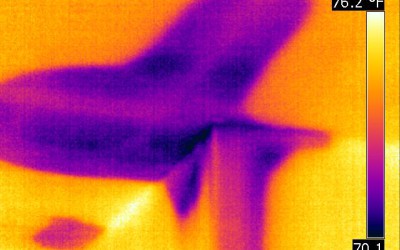
A water damage in the bathroom promotes the growth of mold and carpenter ants |
Sources: Hölldobler , B. and E.O. Wilson. 1996. Travel in ants , a scientific exploration. Edition du Seuil, 247 p.
- Insectariums the city of Montreal .






